Quanti-Max™ (QM10000)
Quanti-Max™ WST-8 Cell Viability Assay Kit (Colorimetric)
| Catalog Number | Unit Size |
|---|---|
| QM1000 | 1,000 tests |
| QM2500 | 2,500 tests |
| QM5000 | 5,000 tests |
| QM10000 | 10,000 tests |
제품설명
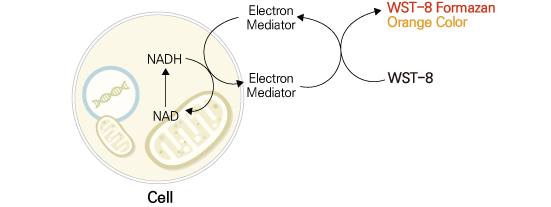
BIOMAX 사의 Quanti-Max™ WST-8 Cell Viability Assay Kit 은 Colorimetric assay 방식으로 세포 증식/독성을 측정할 수 있는 편리하고 민감한 감도를 가지는 제품입니다. 세포내의 Dehydrogenase의 활성에 의해 발생되는 전자를 Electron mediator가 세포막을 자유롭게 이동하면서 배양액 내의 WST-8을 환원시켜 오렌지색의 Formazan을 생성합니다. 물에 녹지 않아 유기용매 (DMSO)가 필요한 MTT assay와는 다르게 물에 잘 녹는 WST-8을 사용함으로써 사용이 편리해지고 세포에 영향을 주는 반응 변수들을 제거한 제품이고 또한 안정적이며 보다 높은 민감성을 갖는 제품입니다.
제품구성
|
Cat. No. |
Components | Size | Storage |
|---|---|---|---|
| QM1000 | 1000 tests | 5 ㎖ x 2 Bottles | 4 ℃ |
| QM2500 | 2500 tests | 5 ㎖ x 5 Bottles | |
| QM5000 | 5000 tests | 25 ㎖ x 2 Bottles | |
| QM10000 | 10000 tests | 25 ㎖ x 4 Bottles |
* 개봉하지 않은 제품은 빛을 차단한 상태에서 4℃ 보관 시 약 1 년간 안정적입니다.
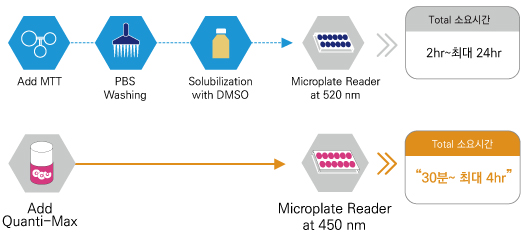
MTT와의 비교
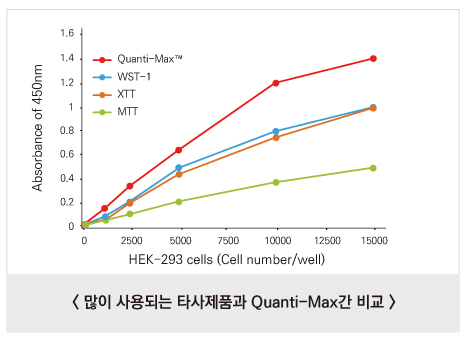
타사와의 비교

제품 안정성 비교 테스트

결과분석

인용논문
1) Choi, B., Kim, J.E., Park, S.O., Kim, E.Y., Oh, S., Choi, H., Yoon, D., Min, H.J., Kim, H.R., and Chang, E.J. (2022). Sphingosine-1-phosphate hinders the osteogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells in association with AKT signaling pathways. Int J Oral Sci 14, 21. 10.1038/s41368-022-00173-5.
2) Chung, C.H., Jung, W., Keum, H., Kim, T.W., and Jon, S. (2020). Nanoparticles Derived from the Natural Antioxidant Rosmarinic Acid Ameliorate Acute Inflammatory Bowel Disease. ACS Nano 14, 6887-6896. 10.1021/acsnano.0c01018.
3) Kwon, K., Cho, H., Lee, S., Cho, E.J., Yu, W., Kok, C.Y.L., Je, H.S., Kim, J.-I., Cho, H.J., and Kwon, T. (2022). Adaptive cellular response of the substantia nigra dopaminergic neurons upon age-dependent iron accumulation. Aging Cell 21, e13694. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.13694.
4) Hwang, C., Choi, M.-H., Kim, H.-E., Jeong, S.-H., and Park, J.-U. (2022). Reactive oxygen species-generating hydrogel platform for enhanced antibacterial therapy. NPG Asia Materials 14, 72. 10.1038/s41427-022-00420-5.
5) Jang, M., Oh, S.W., Lee, Y., Kim, J.Y., Ji, E.S., and Kim, P. (2022). Targeting extracellular matrix glycation to attenuate fibroblast activation. Acta Biomaterialia 141, 255-263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2022.01.040.
6) Keum, H., Kim, D., Kim, J., Kim, T.W., Whang, C.-H., Jung, W., and Jon, S. (2021). A bilirubin-derived nanomedicine attenuates the pathological cascade of pulmonary fibrosis. Biomaterials 275, 120986. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2021.120986.
7) Kim, T.Y., Kim, J.-Y., Kwon, H.C., Jeon, S., Lee, S.j., Jung, H., Kim, S., Jang, D.S., and Lee, C.J. (2022). Astersaponin I from Aster koraiensis is a natural viral fusion blocker that inhibits the infection of SARS-CoV-2 variants and syncytium formation. Antiviral Research 208, 105428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.antiviral.2022.105428.
8) Kang, J.-Y., Kim, H., Mun, D., Yun, N., and Joung, B. (2021). Co-delivery of curcumin and miRNA-144-3p using heart-targeted extracellular vesicles enhances the therapeutic efficacy for myocardial infarction. Journal of Controlled Release 331, 62-73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2021.01.018.